TD-EUA: Task-Decomposable Edge User Allocation with QoE Optimization
Dec 9, 2020·
,
 ,
,
,
,
,
·
0 min read
,
,
,
,
,
·
0 min read
Guobing Zou
Ya Liu
Zhen Qin
Jin Chen
Zhiwei Xu
Yanglan Gan
Bofeng Zhang
Qiang He
Abstract
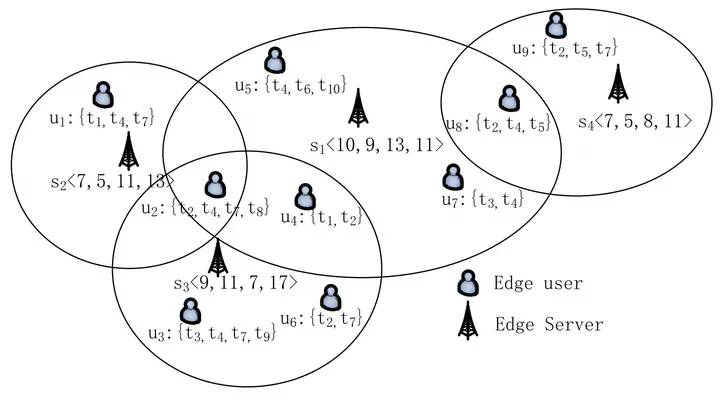
The edge user allocation (EUA) problem has attracted a lot of attention recently. EUA aims at allocating edge users to nearby edge servers strategically to ensure low-latency network connection. Existing approaches assume that a users’ request can only be served by an individual edge server or cannot be served at all. They neglect the fact that a user’s request may be decomposable and partitioned into multiple tasks to be performed by different edge servers. To tackle this new task-decomposable edge user allocation (TD-EUA) problem, we model it as an optimization problem. Two novel approaches named TD-EUA-O and TD-EUA-H are proposed, one for finding the optimal solution based on Integer Linear Programming that maximizes users’ overall Quality of Experience (QoE), and the other for efficiently finding a sub-optimal solution in large-scale EUA scenarios. Extensive experiments based on a widely-used real-world dataset are conducted to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of our approaches. The results demonstrate that our approaches significantly outperform the baseline and the state-of-the-art approach.
Type
Publication
in International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing